환경설정
도커
시작하기에 앞서서 개발 환경이 M1이기 때문에 amd64 환경을 사용하기 위해 llvm-tutor를 도커로 구동하기로 했다.
1
2
3
4
git clone https://github.com/banach-space/llvm-tutor
cd llvm-tutor
docker build . --platform linux/amd64 -f Dockerfile_ubuntu_apt -t llvm/tutor
docker run --platform linux/amd64 -it llvm/tutor
pass 만들기 테스트
pass를 만들기 위해서 필요한 명령어들을 종합하면 다음과 같이 한번에 나타낼 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
mkdir /llvm-tutor/build
cd /llvm-tutor/build
cmake -DLT_LLVM_INSTALL_DIR=$LLVM_DIR ../HelloWorld/
make
$LLVM_DIR/bin/clang -O1 -S -emit-llvm ../inputs/input_for_fcmp_eq.c -o input_for_hello.ll -fno-discard-value-names
$LLVM_DIR/bin/opt -load-pass-plugin ./libHelloWorld.so -passes=hello-world -disable-output input_for_hello.ll
이제 pass를 컴파일 할 수 있게 되었으니 llvm을 학습하고 직접 pass를 만들어보도록 하자.
pass 만들기
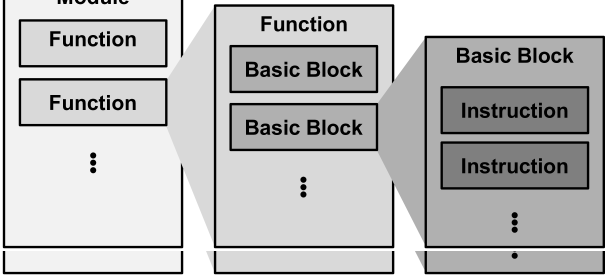
llvm의 구조
llvm은 llvm::Module -> llvm::Function -> llvm::BasicBlock -> llvm::Instruction의 계층적인 구조로 IR을 관리한다.
- Module = 하나의 소스 파일
- Function = 함수
- Basic Block = Branch나 Return 같은 제어 명어로 끝남(이동이 없는 코드의 Block을 의미)
- Instruction = 명령어
llvm pass 만들어 보자
앞서 설명한 것과 같이 Function단위로 파일을 전달 받고 for문을 통해서 BasicBlock을 출력하고 Instruction을 접근 할 수 있다. 아래 코드들을 확인해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// New PM implementation
struct HelloWorld : PassInfoMixin<HelloWorld> {
// Main entry point, takes IR unit to run the pass on (&F) and the
// corresponding pass manager (to be queried if need be)
PreservedAnalyses run(Function &F, FunctionAnalysisManager &) {
errs() << "- Start of function [" << F.getName() << "]\n";
for (BasicBlock &BB : F){
errs() << "- Start of Basicblock ["<< BB.getName() << "], num of instructions [" << BB.size() << "] instructions.\n";
for (Instruction &I : BB){
errs() << "- Instruction : " << I << "\n";
}
}
return PreservedAnalyses::all();
}
// Without isRequired returning true, this pass will be skipped for functions
// decorated with the optnone LLVM attribute. Note that clang -O0 decorates
// all functions with optnone.
static bool isRequired() { return true; }
};
llvm-tutor에서 분기가 가장 많은 input_for_fcmp_eq을 가져왔다. Basic Block의 단위는 Branch나 Return이 없을 때까지의 Instruction의 연속들을 표현한다. 따라서 if와 return이 존재하는 것을 선택했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
double sqrt_impl(double x, double hi, double lo) {
// First direct floating-point equality comparison
if (hi == lo) {
return lo;
}
double midpoint = (lo + hi + 1.0) / 2.0;
if (x / midpoint < midpoint) {
return sqrt_impl(x, lo, midpoint - 1.0);
}
return sqrt_impl(x, midpoint, hi);
}
Basicblcok에서 BB.getName()을 통해서 현재 블럭이 무슨 역할을 하는지 확인한다. 각자의 베이직 블럭에 맞게 확인하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- Start of function [sqrt_impl]
- Start of Basicblock [entry], num of instructions [1] instructions.
- Instruction : br label %tailrecurse
- Start of Basicblock [tailrecurse], num of instructions [4] instructions.
- Instruction : %hi.tr = phi double [ %hi, %entry ], [ %lo.tr, %if.then4 ], [ %div, %if.end ]
- Instruction : %lo.tr = phi double [ %lo, %entry ], [ %sub, %if.then4 ], [ %hi.tr, %if.end ]
- Instruction : %cmp = fcmp oeq double %hi.tr, %lo.tr
- Instruction : br i1 %cmp, label %return, label %if.end
- Start of Basicblock [if.end], num of instructions [6] instructions.
- Instruction : %add = fadd double %hi.tr, %lo.tr
- Instruction : %add1 = fadd double %add, 1.000000e+00
- Instruction : %div = fmul double %add1, 5.000000e-01
- Instruction : %div2 = fdiv double %x, %div
- Instruction : %cmp3 = fcmp olt double %div2, %div
- Instruction : br i1 %cmp3, label %if.then4, label %tailrecurse
- Start of Basicblock [if.then4], num of instructions [2] instructions.
- Instruction : %sub = fadd double %div, -1.000000e+00
- Instruction : br label %tailrecurse
- Start of Basicblock [return], num of instructions [1] instructions.
- Instruction : ret double %lo.tr